Is Solar Highway the Future of Sustainable Infrastructure?
Solar highways, an innovative integration of renewable energy and transportation, hold immense potential for widespread application. They are particularly promising in countries with dense transportation networks and limited land resources. This article explores their practical applications, compares them with traditional ground-mounted solar farms, and identifies the most suitable regions for their development.
Key Applications of Solar Highways
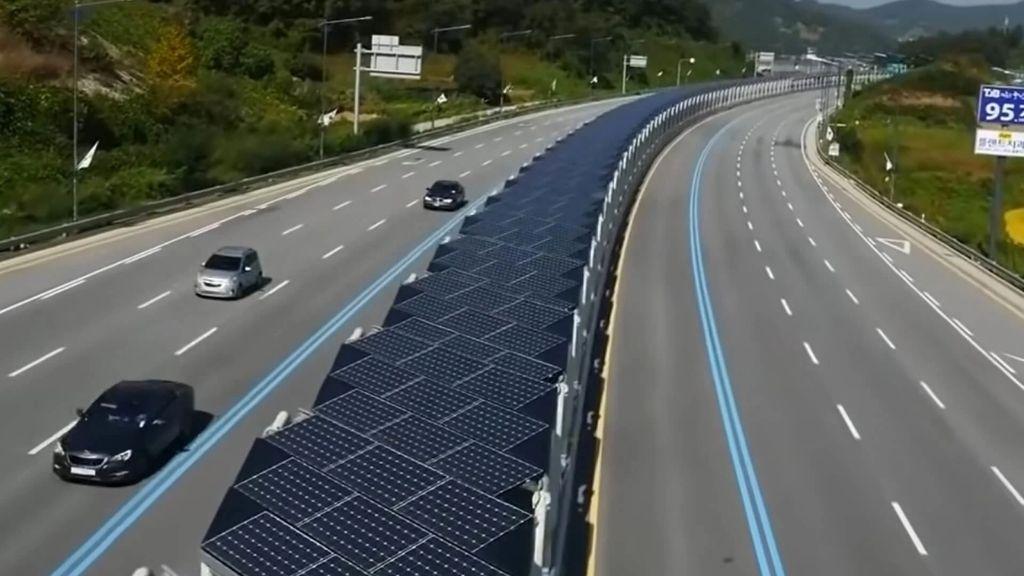

Highways
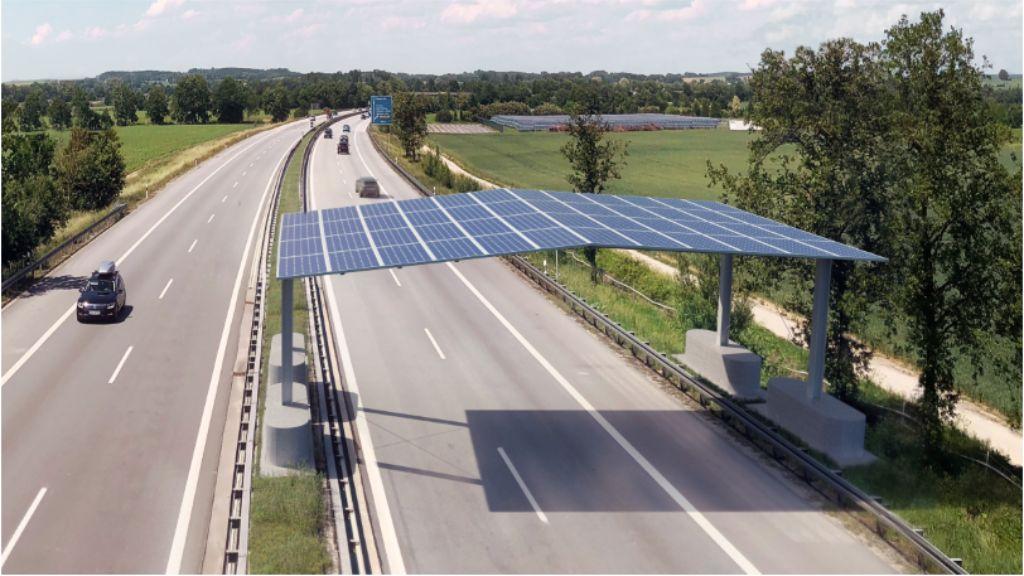
Currently, the most prevalent use of solar highways is in high-speed road networks. In China, the Guizhou Deyu Expressway has installed solar panels at toll stations, service areas, and tunnel entrances to power lighting and ventilation systems while utilizing otherwise idle land. Similarly, Zhejiang's Wentai Expressway incorporates solar farms on slopes and service area rooftops, following a "self-consumption with surplus grid integration" model to reduce electricity costs.
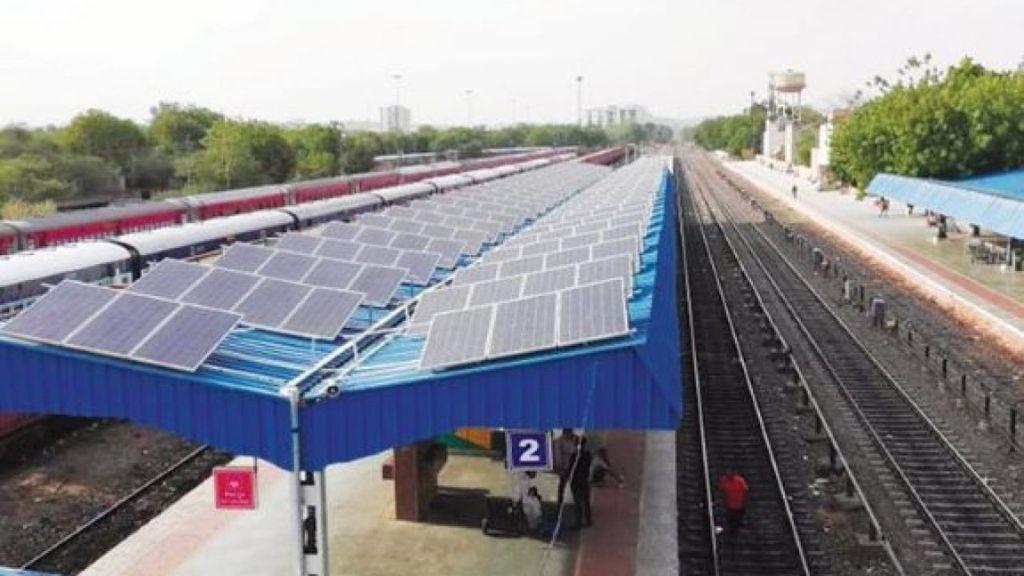

Railways
Though less common, solar panels can be installed along railway lines or station rooftops to power signaling systems and lighting. Shanghai's metro stations have already implemented pilot projects, with potential expansion into the national railway sector.
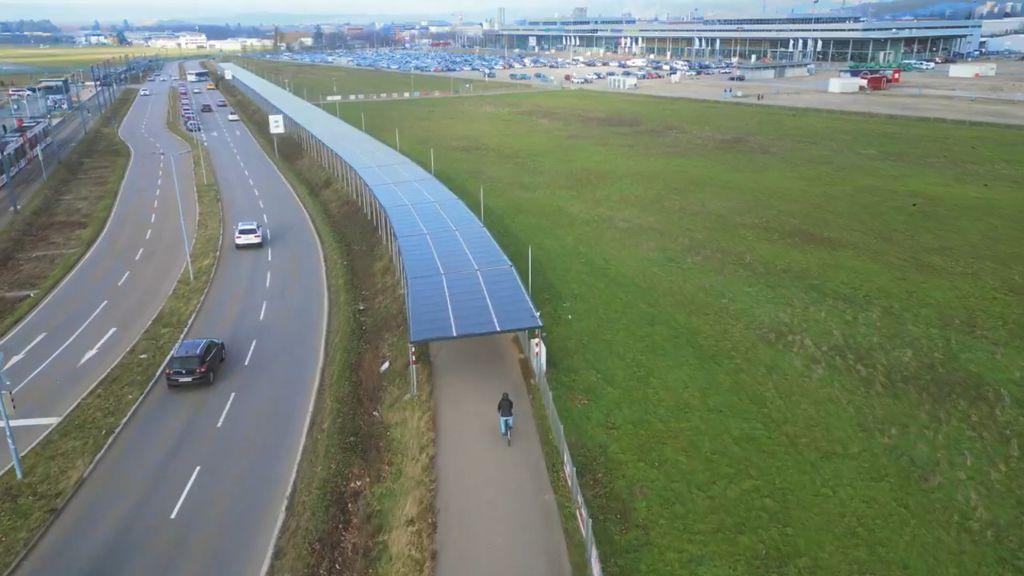

Bicycle Lanes & Pedestrian Walkways
The Netherlands pioneered solar-powered bike lanes, covering photovoltaic panels with durable glass for dual-purpose energy generation and transportation. Meanwhile, China’s Chenhai Highway in Shanghai has integrated solar streetlights, achieving a visually appealing and energy self-sufficient solution.
Comparison: Solar Highways vs. Traditional Ground-Mounted Solar Farms
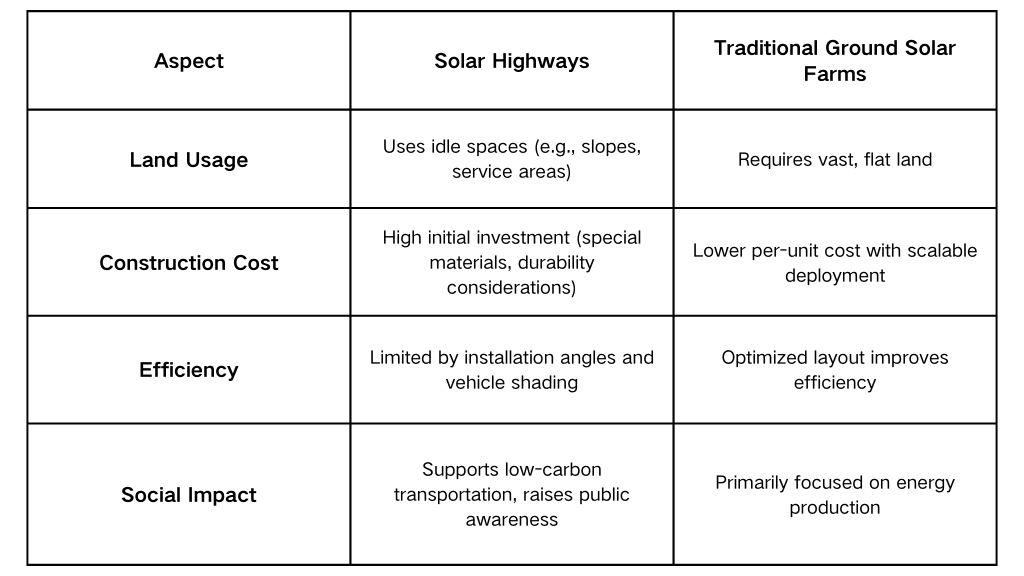
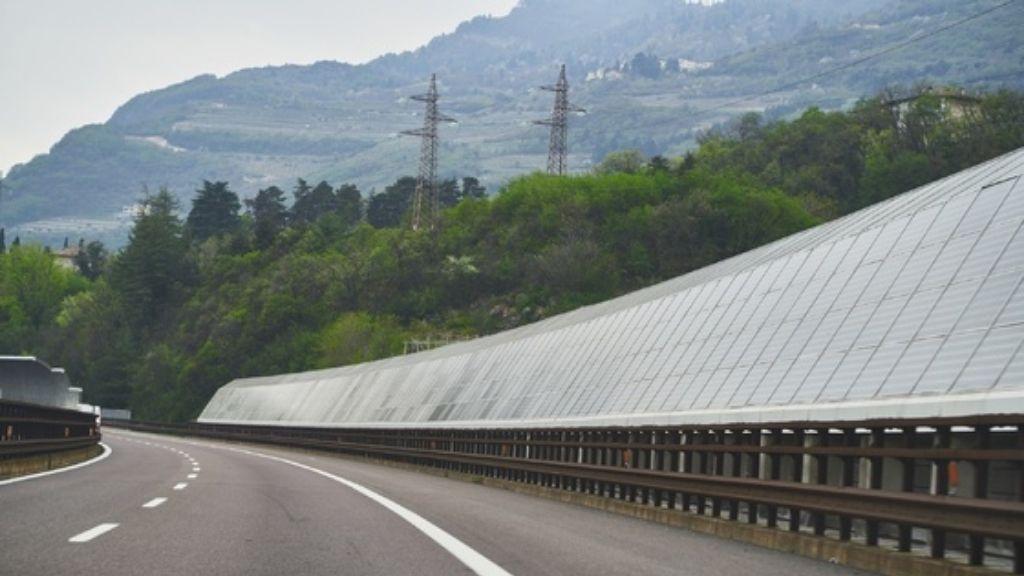
While solar highways maximize land efficiency and support green transportation, they face challenges in cost and maintenance due to wear and tear from vehicular traffic.
Which Countries Are Best Suited for Solar Highways?
China
With the world’s longest expressway network, China is leading solar highway trials in Shanghai, Yunnan, and Guizhou. Government policies strongly support solar-integrated transportation, with Shanghai targeting over 120MW of new solar highway installations by 2025.
Germany & The Netherlands
European nations prioritize renewable energy. The Netherlands built the world’s first solar bike path, while Germany’s dense highway network offers viable locations for further implementation.

Japan
Japan’s compact landmass and high transportation demand make solar highways an efficient way to maximize space usage while reducing reliance on imported energy.
United States
With an extensive highway system and abundant sunlight in states like California, the U.S. is exploring solar-integrated carports and roadways for large-scale adoption.

Conclusion
Despite technical and financial challenges, solar highways represent a groundbreaking approach to sustainable infrastructure. As technology advances and policies evolve, countries with extensive transportation networks and limited land will benefit the most, paving the way for a greener future in global energy transformation.