What is the difference between PV and CSP?
Different Principles
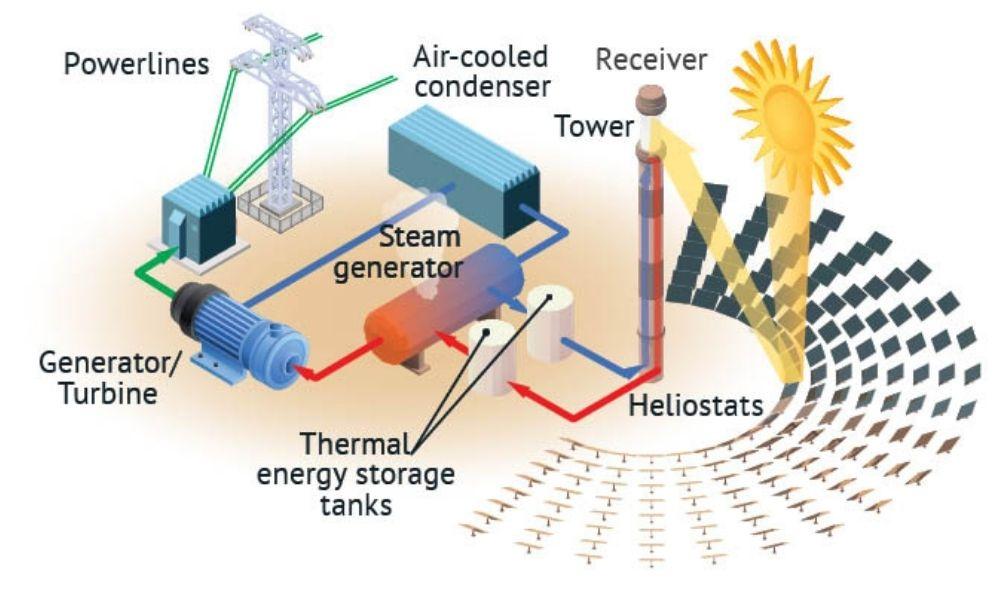
CSP: Concentrated solar power uses mirrors or concentrators to focus the sun's rays onto a collector, which heats a fluid (such as water or oil) to produce high-temperature, high-pressure steam, which then drives a turbine to generate electricity. This process involves the conversion of ‘solar-thermal-mechanical-electrical energy’.
PV: PV power generation uses solar panels to absorb visible light from the sun to form photoelectrons, generating an electric current to generate electricity, which belongs to the category of ‘light energy - electricity’.
Application Scenarios
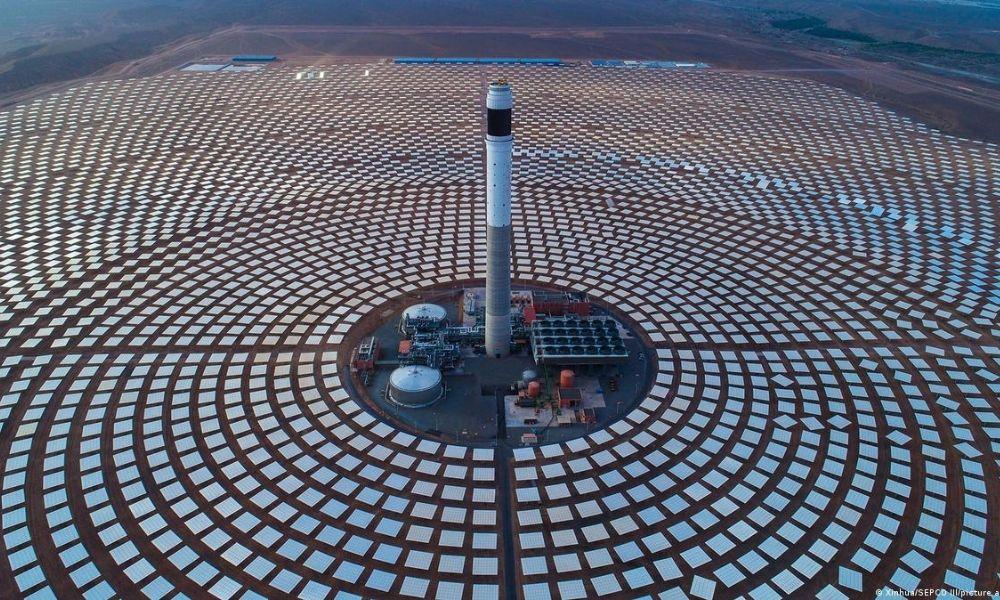
CSP: CSP systems are usually suitable for large-scale power plant construction and can provide large amounts of electricity in a stable manner. They are particularly suitable for regions with large terrain and long hours of light.
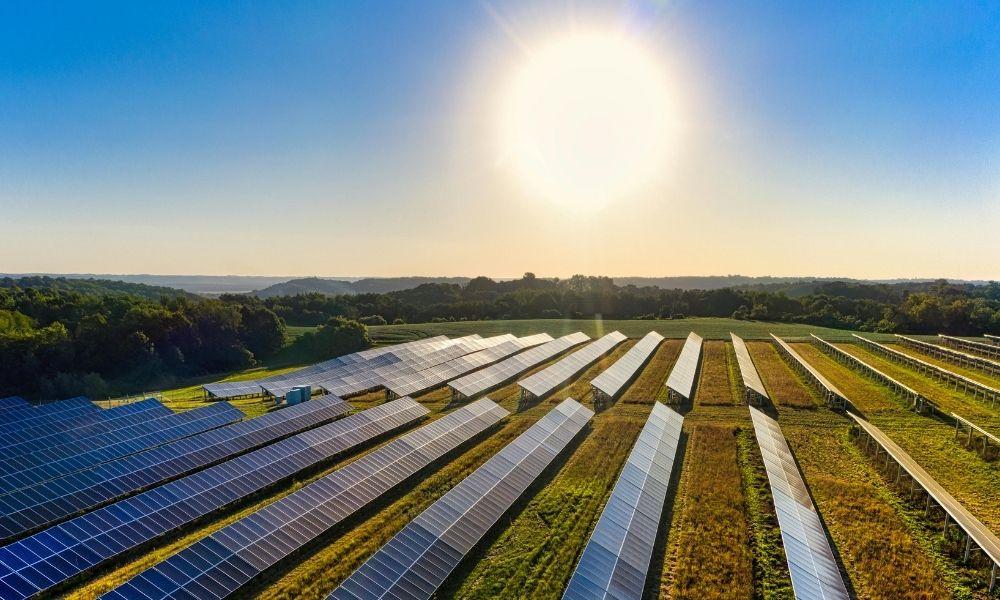
PV: PV systems are used in a wide range of applications such as home rooftops and commercial buildings, in addition to centralized power generation. The flexibility of PV systems allows them to be installed in a wide range of environments.

Efficiency and Costs
CSP: The efficiency of CSP systems is around 35 %, close to the level of thermal power and much higher than PV. Therefore the investment and maintenance costs of the system may be relatively high. The cost per kilowatt for CSP is five times that of PV.

PV: The efficiency of PV systems is relatively low but is improving with technological advances and improved materials. The installed cost of PV systems is decreasing every year, making them increasingly affordable in both the domestic and commercial sectors.
Environmental Impact
Both are clean energy technologies that can reduce dependence on fossil fuels and lower greenhouse gas emissions.
CSP systems, which basically use physical means to convert light energy to electricity, pose minimal environmental hazards but require consideration of water consumption.
PV systems are more flexible, do not require large amounts of water resources, and are suitable for use in arid areas.
Conclusion
CSP and PV have their own advantages and are suitable for different application scenarios and needs. Choosing the right type of solar energy utilization needs to be determined by specific energy needs, geographical location, and economic considerations. With the development of technology and policy support, CSP and PV will play an increasingly important role in the future of renewable energy.