Is east-west direction better for solar systems?
The direction of a solar system installation is one of the key factors affecting the maximum power generation. For example, in the Northern Hemisphere, PV systems are typically installed facing south, while the optimal direction for countries in the Southern Hemisphere is north.

However, in practical applications, the east-west orientation for installing photovoltaics is increasingly accepted due to limitations such as building layouts and available space, especially in residential photovoltaics.
Compared to solar systems installed facing south or north, east-west oriented solar systems have the following advantages:
Extended Inverter Lifespan
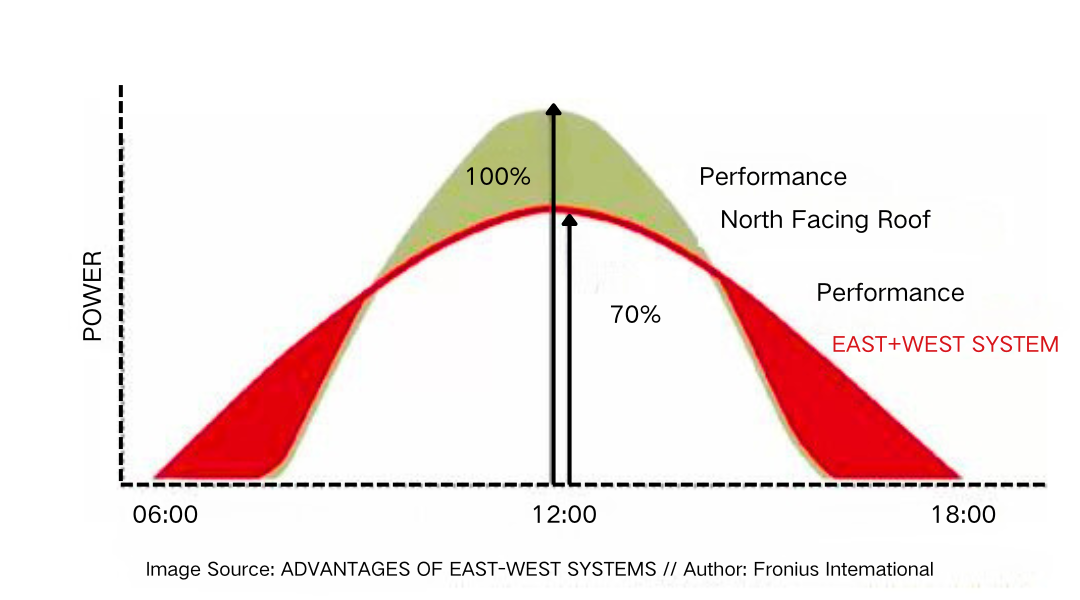
The total output of east-west oriented solar systems is slightly lower than that of south-north oriented systems, but their power generation is more stable throughout the day, avoiding the sharp peaks seen in south-north systems at noon. From the perspective of inverters, this results in more efficient operation and reduces the likelihood of receiving overrated DC sizes, thus extending their lifespan.
High Roof Surface Utilization
Data shows that east-west oriented solar systems make better use of roof surfaces because the solar panels are arranged closely together and slightly inclined in all directions from east and west. This not only effectively utilizes space but also prevents shading between modules.
Increased Power Generation Efficiency
German manufacturer Renusol found that on the same size flat roof, east-west systems generate about 30% more solar energy than south-north systems. Typically, south-north oriented solar panels require greater row spacing to avoid yield loss due to shadows cast by modules. The increased efficiency of east-west systems is due to their lower tilt angle (around 10°), allowing for no gaps between rows, which significantly increases the utilization of roof space. Consequently, the annual feed-in power will also increase.
Reduced Installation Costs
East-west systems can be more effective in reducing installation costs. Since there are virtually no gaps between the solar panels, fewer structures and connecting cables are required, saving 24% on pile foundations and steel structure installation costs.
Decreased Wind Load Pressure
Due to the back-to-back modules, east-west PV systems are less affected by wind loads. Additionally, the installation height and tilt angle are lower than those of south-north systems, reducing exposure to winds from the north and south through a smaller tilt angle and aerodynamic design, creating a streamlined and calm internal environment.
Reduction Of Load Pressure
In addition to reducing wind load pressure, east-west PV systems also save on ballast. With smaller structural dimensions and tilt angles, there is no need for wind deflectors like those required for south-north modules. Therefore, roof loads will be less stressful and more evenly distributed than traditional fixed tilt systems.
As stated above, for users looking to supplement grid power with solar energy during peak hours, using an east-west solar systems is an effective solution. As it allows for the storage of solar energy during other times in a battery for later use, saving on electricity costs.