What Solar Panels are Suitable for Agrivoltaic Systems?
As renewable energy develops, agrivoltaics as an innovative land use model is gradually attracting widespread attention. In the initial design of agrivoltaic projects, the selection of suitable photovoltaic (PV) modules is particularly important.
Bifacial Solar Panels: The Preferred Choice to Improve Power Generation Efficiency
Bifacial solar panels, which can generate electricity from both the front and back surfaces, have become a popular choice for agrivoltaic projects. Farmlands often have a relatively high albedo, especially when planting light-colored crops or covering the ground with reflective materials. This reflected light can be effectively utilized by the back surface of bifacial panels, thereby improving the overall power generation efficiency.
For example, when planting crops such as wheat and corn, the high reflectivity of the ground surface can significantly increase the power generation from the panel's backside. This not only makes effective use of the natural light source, but also brings more power generation income to the farmers. In addition, bifacial panels have higher durability and typically have a longer service life, making them suitable for long-term operation in agrivoltaic projects.
Semi-Transparent Solar Panels: Balancing Crop Lighting Needs
In agrivoltaic projects, lighting is a key factor for crop growth. Therefore, selecting components that can balance photovoltaic power generation and crop lighting needs is particularly important. Semi-transparent solar panels are designed to meet this demand. This type of panel allows a portion of the light to pass through and reach the crops on the ground, ensuring they receive sufficient sunlight.
For example,semi-transparent solar panels are usually suitable for crops that require more sunlight, such as fruits and vegetables. These crops are more sensitive to light, and semi-transparent panels can continue to generate photovoltaic power without significantly affecting crop growth, thereby achieving a win-win situation for agricultural production and energy production.
Adjustable-Angle Solar Panels: Optimizing the Relationship between Photovoltaics and Agriculture
The seasonality and crop diversity of agrivoltaic projects require a certain degree of flexibility in the PV modules. Adjustable-angle solar panels can be adjusted in angle based on the sun's position, crop growth cycle, or other environmental factors, thereby optimizing the relationship between photovoltaic power generation and agricultural production.
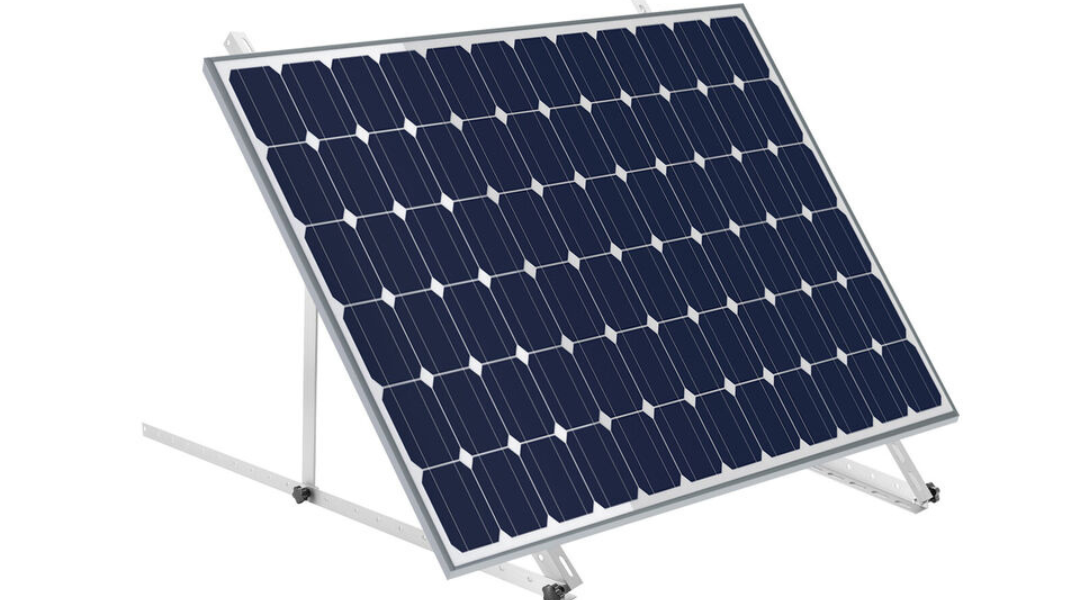

For example, during the winter when daylight hours are shorter, the panels can be adjusted to a more favorable position to maximize power generation. In the summer, the panels can be adjusted to provide more shading to protect crops from excessive light exposure. Through this flexible adjustment, agrivoltaic projects can better adapt to different environmental conditions and achieve efficient land utilization.
Elevated Solar Panels: Suitable for Large Farmlands and Mechanized Operations
For large farmlands or agricultural scenarios that require mechanized operations, elevated solar panels are an ideal choice. These panels are typically installed on higher supports, allowing agricultural machinery to freely pass underneath the panels for tasks such as plowing, sowing, and irrigation. The elevated design ensures that crops receive sufficient light and growth space, while also not interfering with photovoltaic power generation.

This layout is particularly suitable for large-scale farms or crops that require frequent use of agricultural machinery, such as rice fields and corn fields. Elevated solar panels not only improve land utilization, but also provide farmers with greater flexibility, making them suitable for large-scale and long-term promotion.
Weather-Resistant Solar Panels: Ensuring Long-Term Stable Operation
Agrivoltaic projects are often located in rural areas, which may experience extreme weather conditions such as strong winds, rain, snow, and hail. Therefore, the weather resistance of the solar panels is a key factor affecting the long-term stable operation of the project. Selecting PV modules with strong weather resistance, wind pressure resistance, and impact resistance can effectively reduce maintenance costs and ensure the sustainable development of the project.
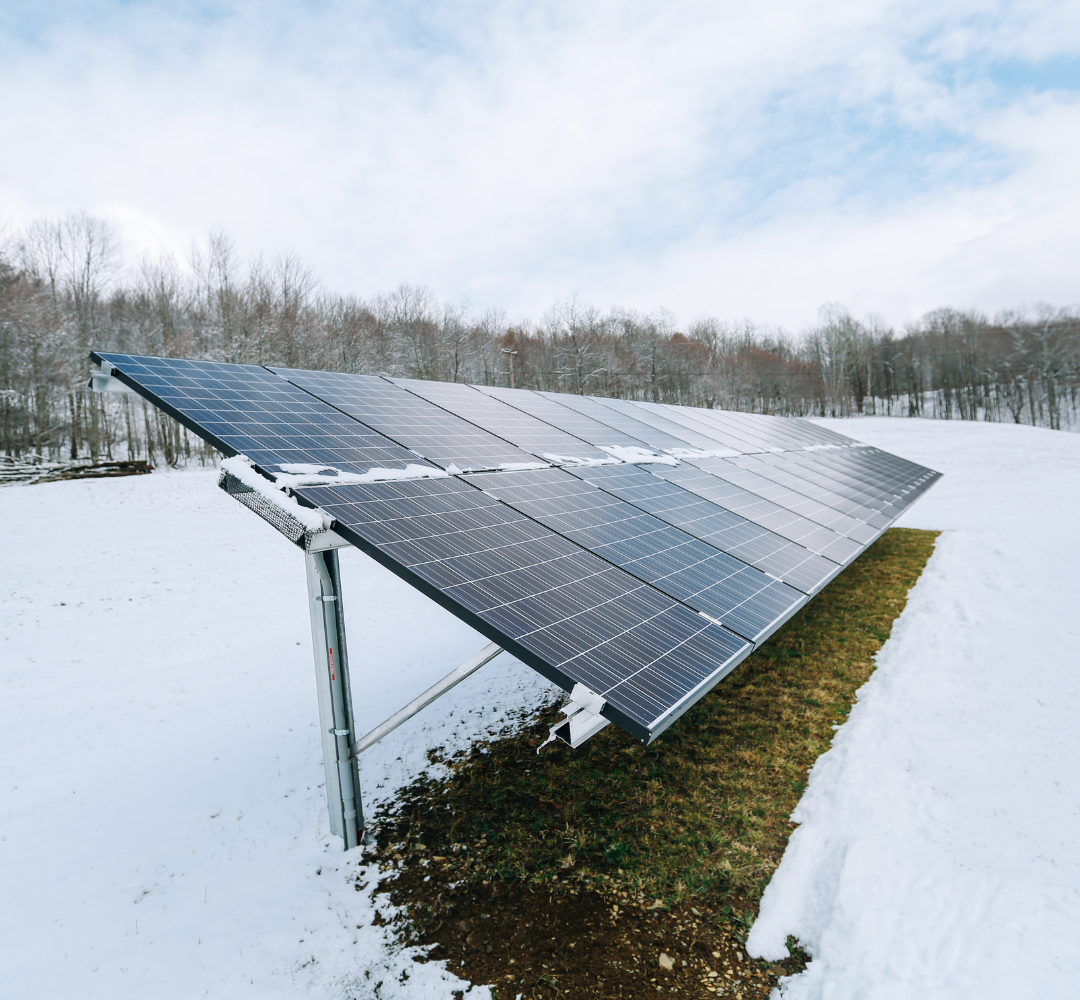

In addition, solar panels with self-cleaning functions are also a good choice. These panels can reduce the accumulation of dust and debris, maintain high power generation performance, and reduce maintenance frequency.
Conclusion
In agrivoltaic projects, the selection of PV modules directly affects the success or failure of the project. Bifacial solar panels, semi-transparent solar panels, adjustable-angle solar panels, elevated solar panels, and weather-resistant solar panels all have their own advantages and are suitable for different application scenarios and needs. By reasonably selecting and combining these components, agrivoltaic projects can not only maximize the utilization of land resources, but also create substantial economic benefits for farmers and investors, promoting the coordinated development of renewable energy and agriculture.